 Ornithine
can react with carbamyl phosphate to form citrulline.
Ornithine
can react with carbamyl phosphate to form citrulline.The results of experiments in which arginine is added to the incubations are unexpected. Therefore, it would seem to be sensible to look at the effect of adding the product of arginase action, ornithine, to incubations with and without a range of concentrations of ammonium.
 Ornithine
can react with carbamyl phosphate to form citrulline.
Ornithine
can react with carbamyl phosphate to form citrulline.
In the simulation you will investigate the effect of adding three different concentrations of ornithine to isolated liver cells incubated with a range of concentrations of ammonium. You will be given results for not only the amount of urea formed, but also the amount of ammonium remaining. Think about the results very carefully.
Can you explain your observations?
The results of experiments in which ornithine is added may also differ from your expectations, so it might be sensible to try the effect of adding the product of the reaction of ornithine with carbamyl phosphate, citrulline.
Citrulline can react with aspartate to form the compound argininosuccinate: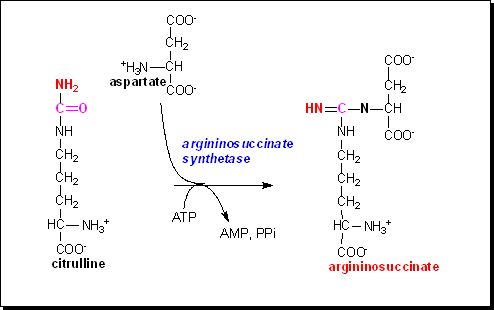
In the simulation you will investigate the effect of adding three different concentrations of citrulline to isolated liver cells incubated with a range of concentrations of ammonium. You will be given results for not only the amount of urea formed, but also the amount of ammonium remaining. Think about the results very carefully.
Can you explain your observations?
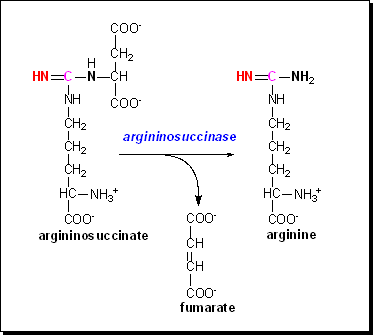 Argininosuccinate
can undergo cleavage to remove what had been the carbon skeleton of aspartate
as fumarate, leaving arginine.
Argininosuccinate
can undergo cleavage to remove what had been the carbon skeleton of aspartate
as fumarate, leaving arginine.
You should now be able to put together the complete pathway of synthesis of urea from ammonium.
You will notice that while the simulation permits you to work with varying concentrations of ammonium, and various concentrations of arginine, ornithine or citrulline, there is no stage at which you consider the addition of aspartate, yet it is obvious from the diagram of the argininosuccinate synthetase reaction above that aspartate is a substrate, and provides one of the two nitrogen atoms of urea.