Back---You may experience viewing problems from scrolling up and down the page, refresh the page to fix this problem. If the problem continues use the stand alone version.
Doppler Shift
Instruction Manual
Introduction
This simulation models magnetic radiation waves being emitted from a moving source. Each wave front is represented as a line. Because this is a model, the frequency of the wave front emitted is not to scale.
Interface
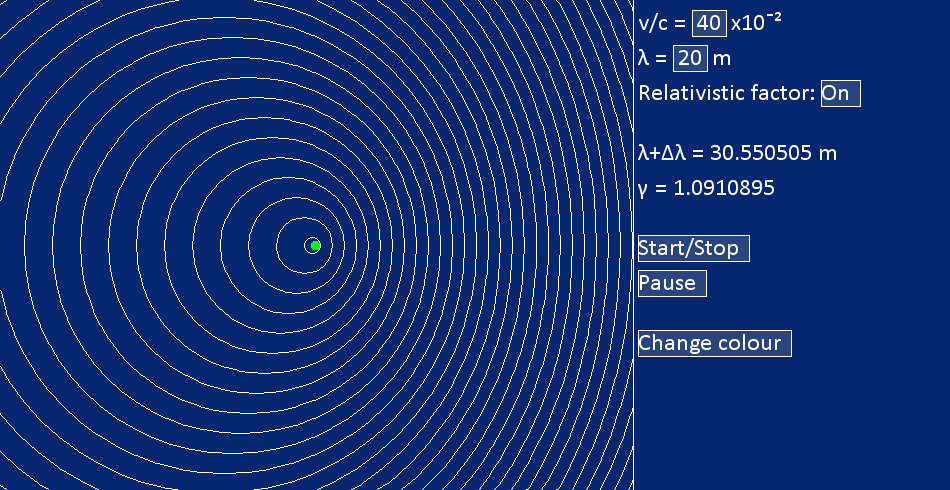
The interface in this simulation consist of two sides, the left hand side shows the simulation and the right hand side shows the control panel. The status bar on the browser displays the frame rate the simulation is performing, a frame rate of 30 is considered satisfactory.
| Simulations functions | Diagram 1 |
|---|---|
| The source of radiation is represented as a green spot. |  |
| Wave fronts are represented as lines. This is where a part of the wave goes through one full phase rotation. |  |
| Control panel functions | Diagram 1 | Diagram 2 |
|---|---|---|
Speed of the sourceThe speed of the source over the speed of light is as shown in diagram 1.It can be edited as shown in diagram 2, click on it and press backspace to delete the variables. Press the number keys to change the variable. Hit enter to return the variable. |
 |
 |
Wavelength of the magnetic radiationThe wavelength of the magnetic radiation s as shown in diagram 1.It can be edited as shown in diagram 2, click on it and press backspace to delete the variables. Press the number keys to change the variable. Hit enter to return the variable. |
 |
 |
Relativistic factorThe relativistic can be considered or ignored in this simulation by turning it on or off. The value of the relativistic factor is as shown in diagram 1.It can be turned on or off in the drop down menu as shown in diagram 2. |
 |
 |
Stretched wavelengthThe length of the stretched wavelength is as shown in diagram 1. |
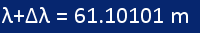 |
|
Start/stop buttonThe start/stop button will start or stop the simulation. |
 |
|
Pause/play buttonThe pause/play button will pause or unpause the simulation. |
 |
|
Change colour buttonThe change colour button changes the colour scheme of the simulation from a selection of :
|
 |
Background physics
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift is the result of a wave emitting source to move causing the wavelength of the wave to stretch or compress. Waves being stretched are known to undergo red shift as their wavelengths has increased towards the red end of the spectrum. The factor of Doppler shift can be derived as shown below.
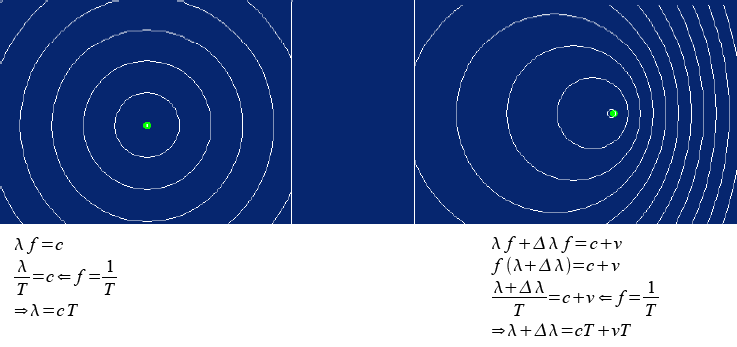
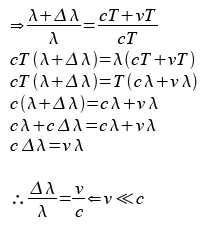
The equation derived is know as the Doppler shift factor and it is used to work out how much the wavelength has been stretched. Notice v has to be much smaller than c because time dilation happens when approaching the speed of light, this is where the rate of time slows down so the waves rotating phasers rotate slower and so their wavelengths are stretched even more. The Doppler shift factor ignores time dilation so v has to be smaller than c for the factor to work.
To work out how long is the stretched wavelength considering time dilation, the relativistic factor is used and it is to be multiplied to the length of the overall stretched wavelength worked out by using the Doppler shift factor as shown below.
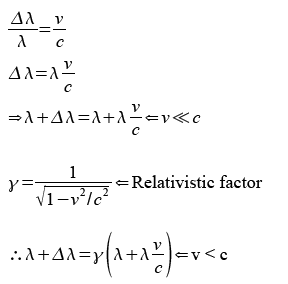
The simulation also uses the same equation as above to work out the length of the stretched wavelength. Try and get the same results using your calculator.
Scientific FAQ
-
What so important about the Doppler Shift?
- It is important because ALL galaxies emit red shift or waves which are stretched. This means all galaxies are moving away from us and using the Doppler Shift factor enable us to work out how fast they are receding away from us.
- Because all galaxies are receding away from us it meant all the galaxies came from one place so the Big Bang theory was concluded.
-
Why is time dilated when approaching the speed of light?
- Time dilation is the result of the speed of light always being constant no matter the velocity of the observer is.
-
What is the point of turning the relativistic factor on and off?
- It helps you to compare how much the relativistic factor has an effect on the stretched wavelength when approaching the speed of light. By entering v/c = 0.99 into the simulation, the value of γ reaches a magnitude of 7!
Technical FAQ
-
Why won't the simulation start?
- You need to press the Start/Stop button to start the simulation.
-
How do I change the variables in the control panel?
- Click on the number box and it should change colour. Press backspace to delete the digits and type in the desired value by typing in the number keys on the keyboard then press enter.
-
Why is my calculator result slightly different from the simulation result?
- Sometimes there will be a rounding error when the simulation converts binary to deanery. If your answer is around the same magnitude, you more or less have the correct answer.