CASA Working Paper 57
1 July 2002
Delivering light-weight online geographic information analysis using ArcIMS
As of July 9, 2002, more than 300 websites, which provide automated mapping and facilities management over the internet, are registered in the ESRI Internet Map Server (IMS) user registry [1]. But it won't be an exaggeration to assume that this is only a tiny fraction of the actual number of IMS sold and used over the world. In fact, realising the potential scope and issues of this new form of geographic information delivery, the International Cartographic Association has formed a Commission dedicated to Maps and the Internet [2].
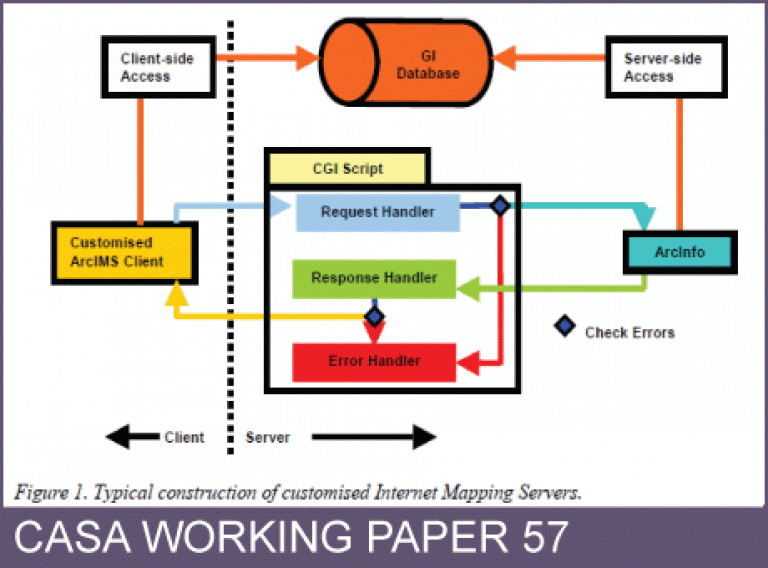
The IMS software has also kept pace with the growing demand and progress in technology. IMS has evolved from the simple HTML image maps to sophisticated servelet-driven mapping services. During this period, a very significant event happened with the arrival of ArcIMS. With the ArcIMS the use of IMS changed from merely an interactive visualisation and query of the spatial databases to a platform for sharing remote spatial databases. In other words, the ArcIMS made the scale of operation of IMS global. While the accessibility and usability of the IMS have certainly increased in the past 5- 6 years, the functionalities provided by IMS however remained fairly static. A widely felt but unreported criticism of IMS has been that the lack of a broader range of spatial analysis functions (except the usual buffering) in the off-the-shelf IMS installation. Therefore a couple of eyebrows always tend to rise if the word 'Internet GIS' is used for IMS. Oddly enough, the ArcIMS 3.x and the older versions carry this limitation as well. Essentially, IMS suffer from the limitation for not being able to allow simultaneous update and dynamic manipulation of the thematic content of the online maps. For example, in the case of ArcIMS while there are provisions for complex scale-dependent rendering, it is not easily possible to manipulate (for example add layers or delete layers) the crucial axl file of a mapping service on the fly. The recent launch of ArcIMS 4 promises to bridge this gap by allowing an enhanced integration with the ArcGIS. The aim of this article is to propose a generic framework, which makes the link between an IMS and a standard GIS, to provide geographic analysis in online maps. We will take the example of such a framework developed for ArcIMS.
This working paper is available as a PDF. The file size is 293KB.
Authors: Sanjay Rana
Publication Date: 1/7/2002
 Close
Close

