Why do we need a Quality Management System (QMS)?
- We must meet the regulatory requirements for all products that we sell.
- We need to meet customer expectations by producing high quality and consistent products that are SAFE.
- A QMS enables us to demonstrate through evidence that we are producing products that meet the required reliability and test criteria.
- We are using controlled manufacturing methods.
- We take action if there is a problem (through a managing non-conformity procedure).
- We consider risk throughout the design and development process etc.
- We monitor device performance.
- We audit what we are producing to continuously improve our ways of working/device.
ISO 13485:2016
For medical devices the QMS ISO standard that is often used is ISO 13485. This international standard specifies the requirements for a QMS where an organization needs to demonstrate its ability to provide medical devices and related services. It is split into different clauses:
- Clauses 0-3 are:
- Introduction to a QMS
- Scope
- Normative references
- Terms and definitions
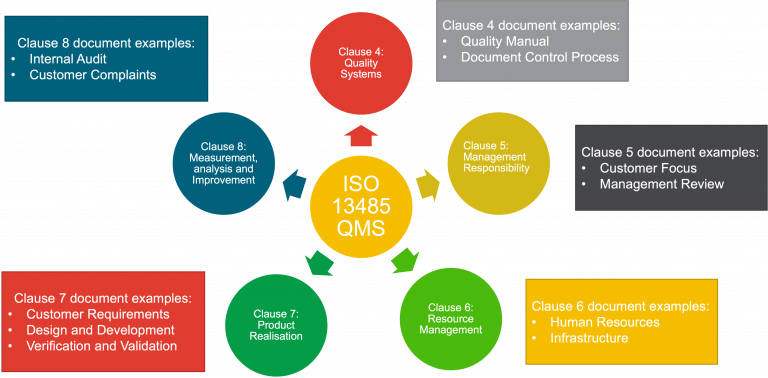
- Clause 4 relates to the Quality Management System
- Clause 5 relates to Management Responsibility
- Clause 6 relates to Resource Management
- Clause 7 is Product Realisation
- Clause 8 is Measurement, Analysis and Improvement
- ISO 13485-QMS requirements example documents
- A strategy for regulatory compliance and procedures for modifications to the device
- Identification of and addressing applicable General Safety and Performance Requirements (GSPR's)
- Responsibility of management
- Resource management, including selection and control of suppliers and sub-contractors
- Risk management
- Clinical evaluation including Post Market Clinical Follow-up
- Product realisation, including planning, design, development, production and service provision
- UDI assignments and labelling
- Setting-up, implementation and maintenance of a post-market surveillance system
- Communication with competent authorities, notified bodies, other stakeholders
- Processes for reporting of serious incidents
- Management of corrective and preventative actions and verification of their effectiveness
- Processes for monitoring and measurement of output, data analysis and product improvement
A QMS is usualy structured like the diagram below:
Top Level Policies
- These are a series of higher levels documents that cover all areas of the QMS.
- They detail how we ensure compliance to regulations, legislation and standards.
- All documents within the QMS should comply to top level policies.
Processes
- These are documents which are instructions on how to conduct a particular action. This can include manufacture instructions or methods of how to conduct an internal audit or management review.
- We must carry out actions as they are described in these documents.
Forms/Records
These are records that form the actual evidence that we have followed a process/policy in a compliant way. They also provide traceability.
Types of Records
Examples include:
- In the development stage, the data generated shows that the device is fit for purpose and has met the regulations for use.
- During manufacturing, we note how we tested the manufactured product.
- To evaluate our suppliers a record is taken of approved suppliers.
- We also have compliant handling records to document investigations.
Document control
Is a key requirement in a QMS. All Quality Systems documents must be controlled as part of the Quality Management System.
All controlled documents have:
- Unique document numbers
- Revision numbers
- Numbered pages
All individuals working within a QMS have te responsibility to ensure good document control is maintained for traceability purposes. You can find out more about document control here.
Audits
- Audits are required to demonstrate compliance as well as continuous improvement of the QMS and device.
- Internal audits will be carried out on a regular basis as part of ISO 13485:2016.
- External audits are carried out by external bodies such as The British Standards Institute (BSI) to ensure that compliance to ISO 13485:2016 is maintained.
- You should expect audits to be a regular occurrence when working/managing a QMS.
Operating a QMS
- Keep it simple and start small
- Start early to get people used to 'processes'
- Only introduce processes that are needed - you need to maintain and use them
- Ensure management reviews cover QMS requirements
 Close
Close

