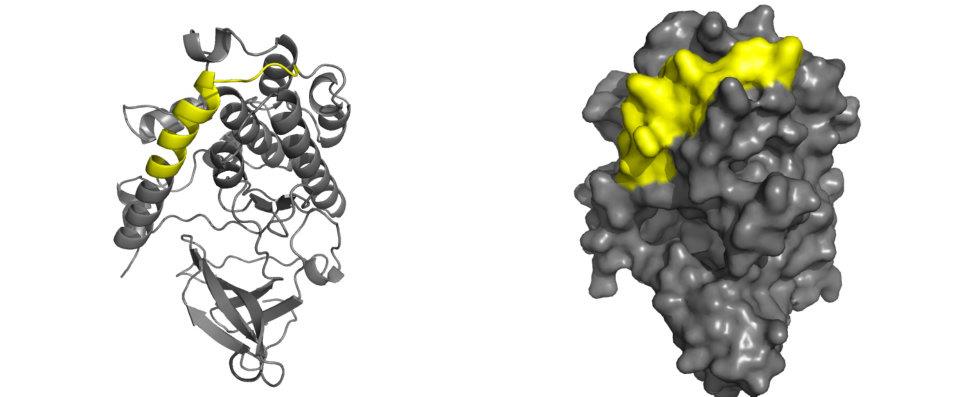
The PP2A binding domain (yellow highlight) is found at the C-terminal helix of the predicted model and is overlapping with the autoinhibitory domain. This domain is crucial for the regulation of CaMKIV activity. Physical association between the PP2A binding domain and PP2A is responsible for the inactivation of CaMKIV (which is achieved through dephosphorylation of the autophosphorylated residues at Thr200 in the active site of CaMKIV) and the maintainence of inactivated CaMKIV in its inactive state. In its inactive state the PP2A domain acts as a part of the active site-blocking helix. Upon activation, this domain moves into a new position to allow ATP and substrate peptide to bind to their respective targets within CaMKIV. |
Weiyi Yao, Havva Yalinca, Jonathan Swain, Josep Monserrat Sanchez, Ann-Marie Tong, Ji Lee, Michele Frison, Sebstian Boissier